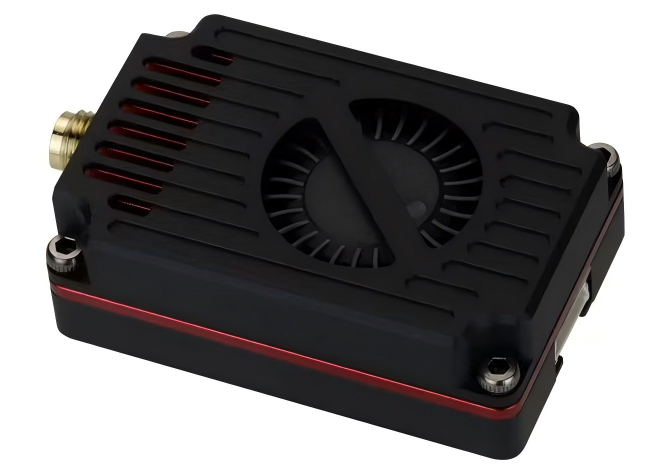
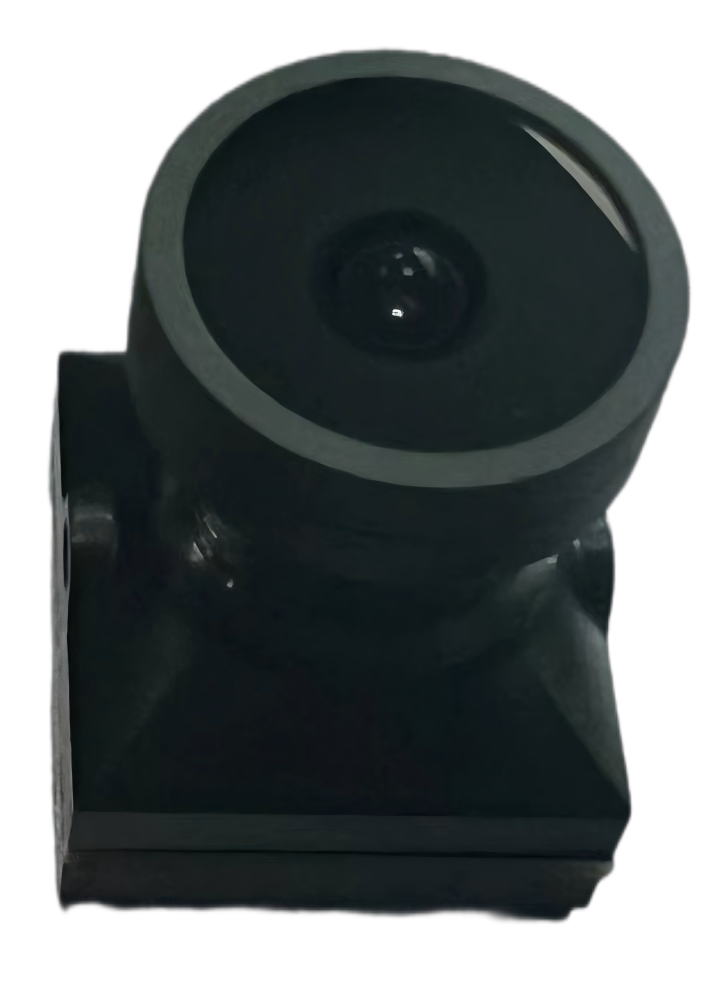
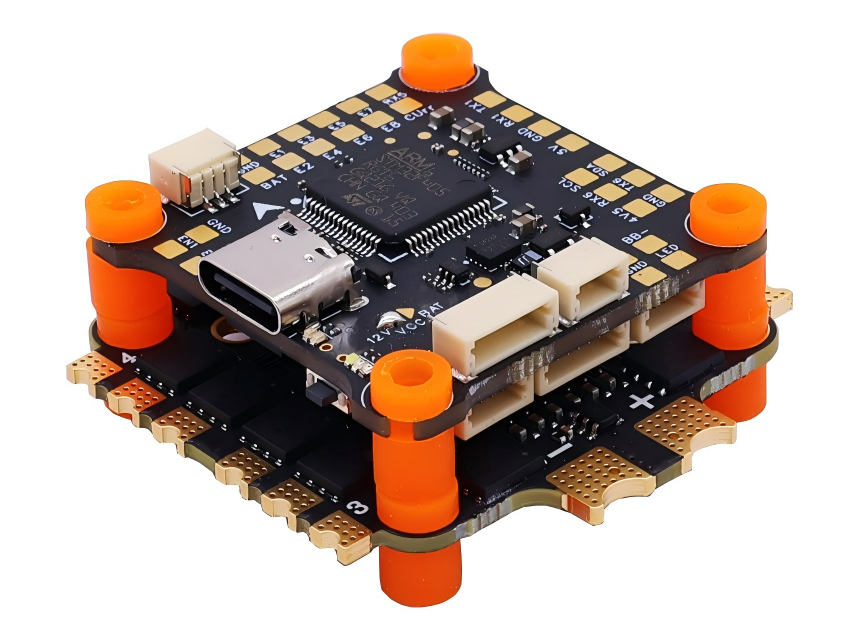
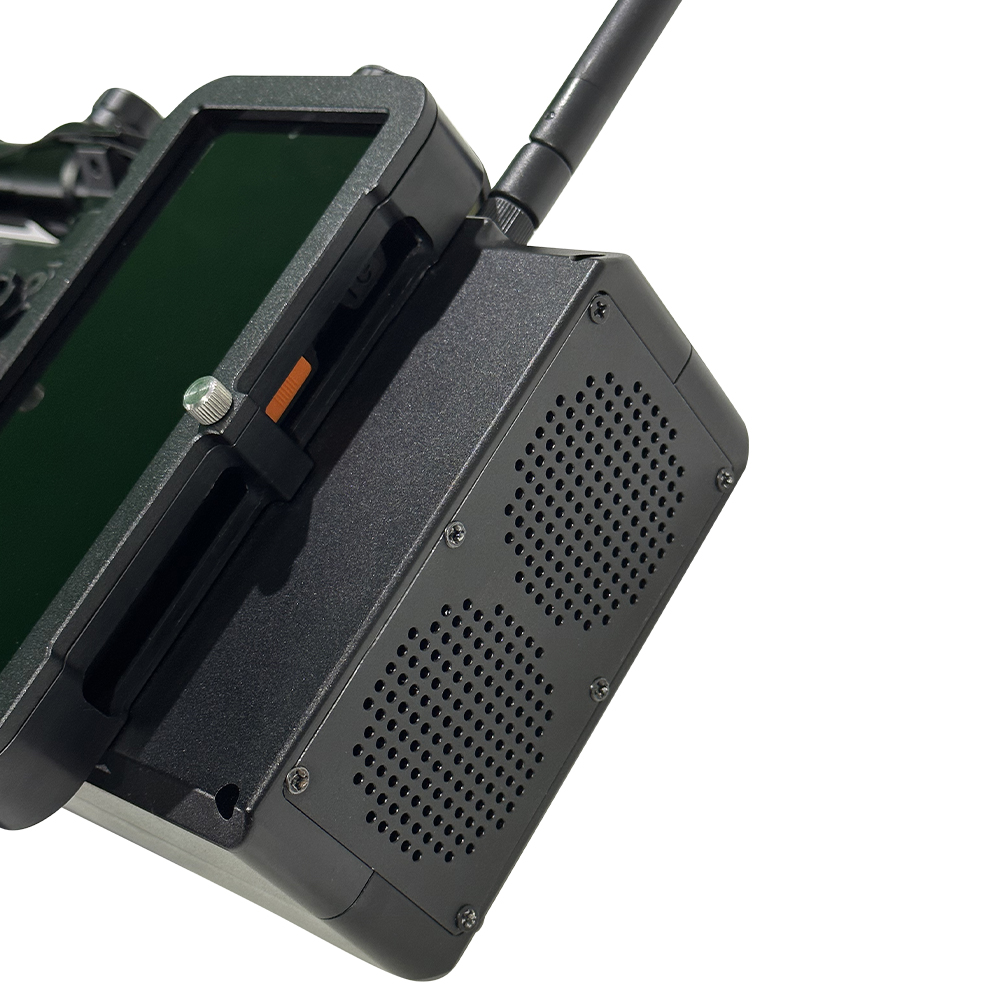
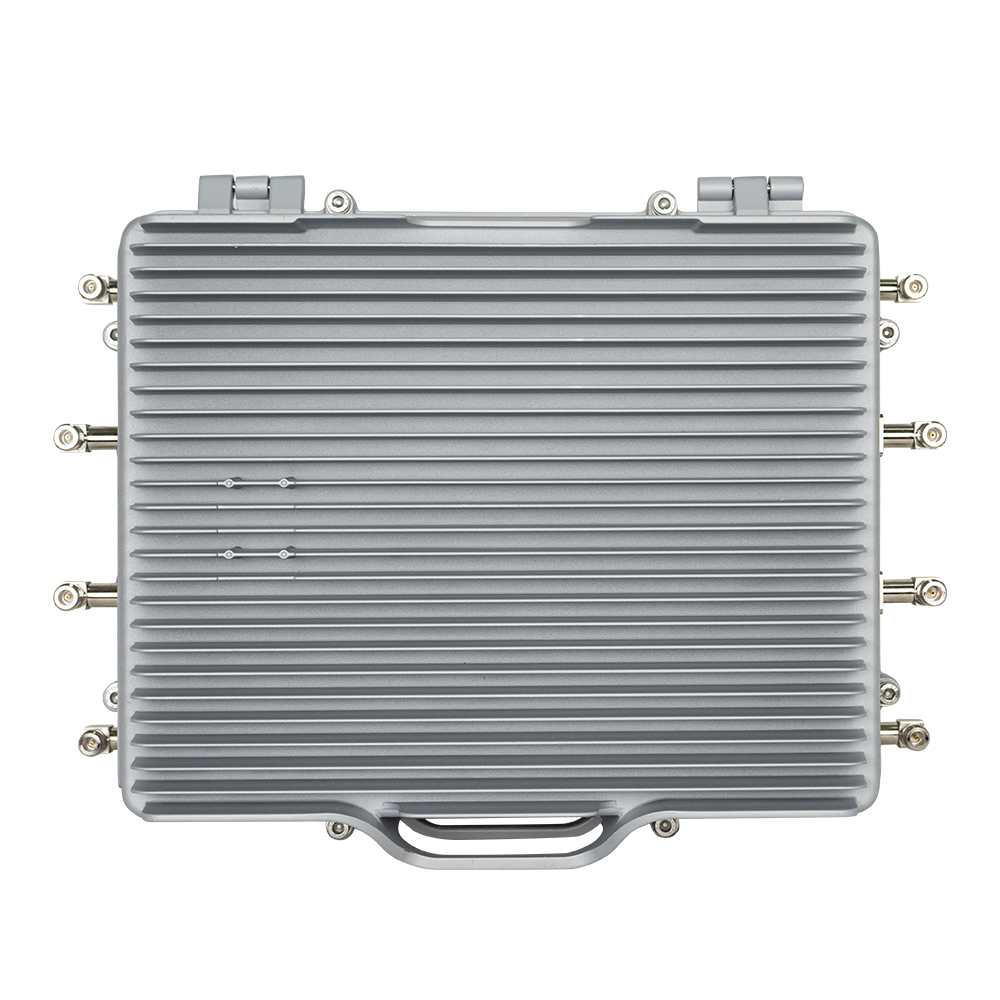
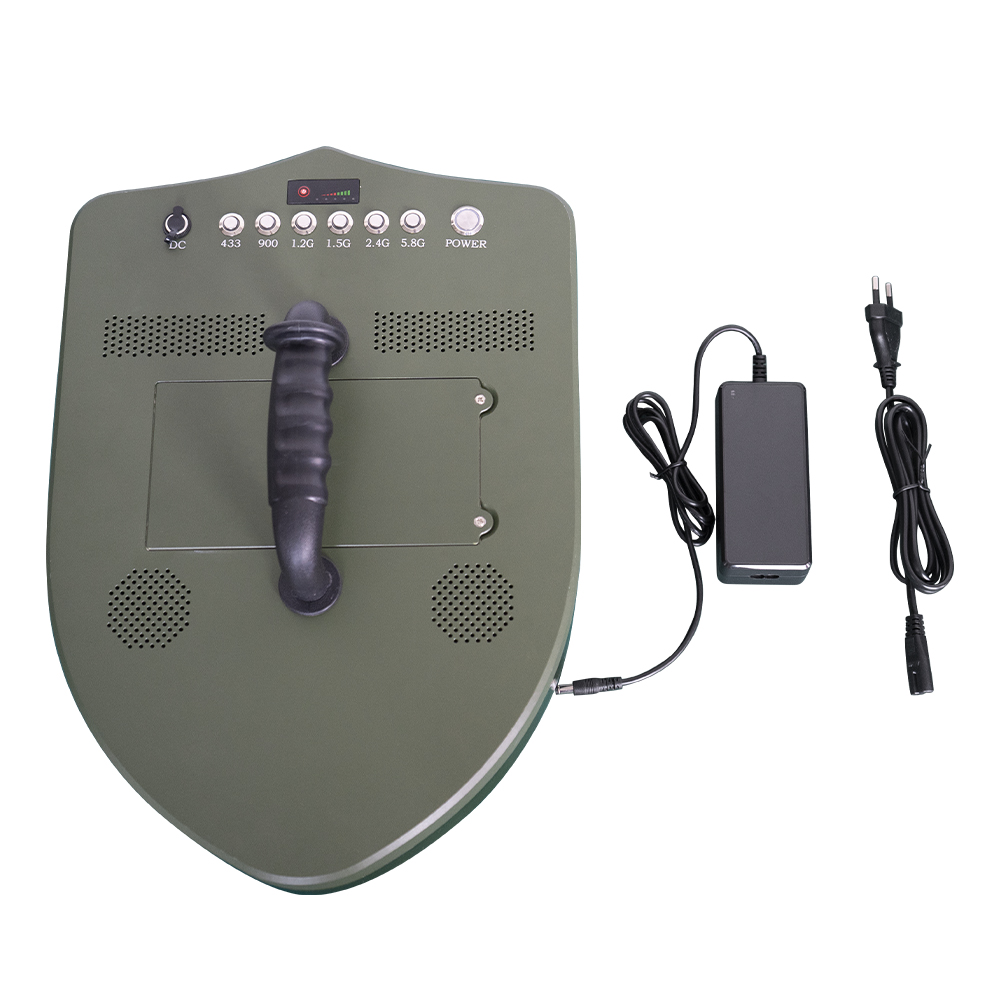
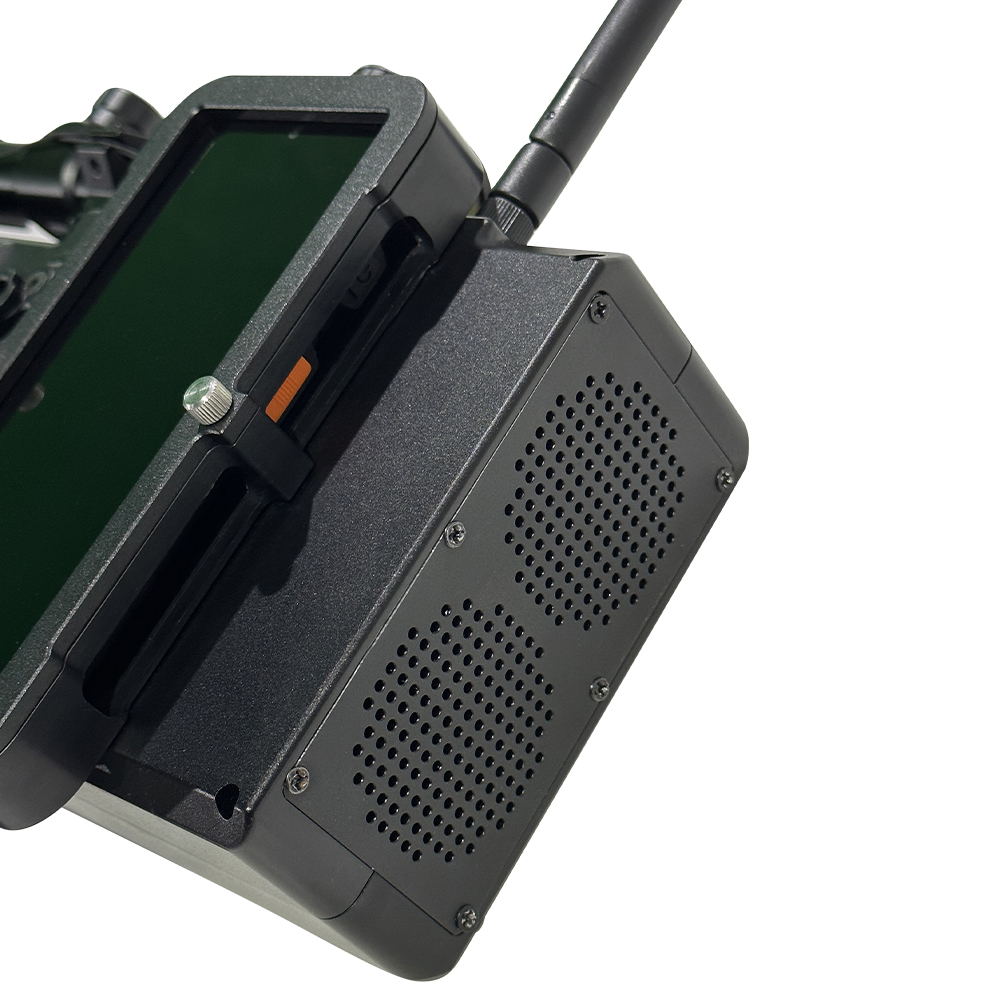
Products
hot sale
Brand
News

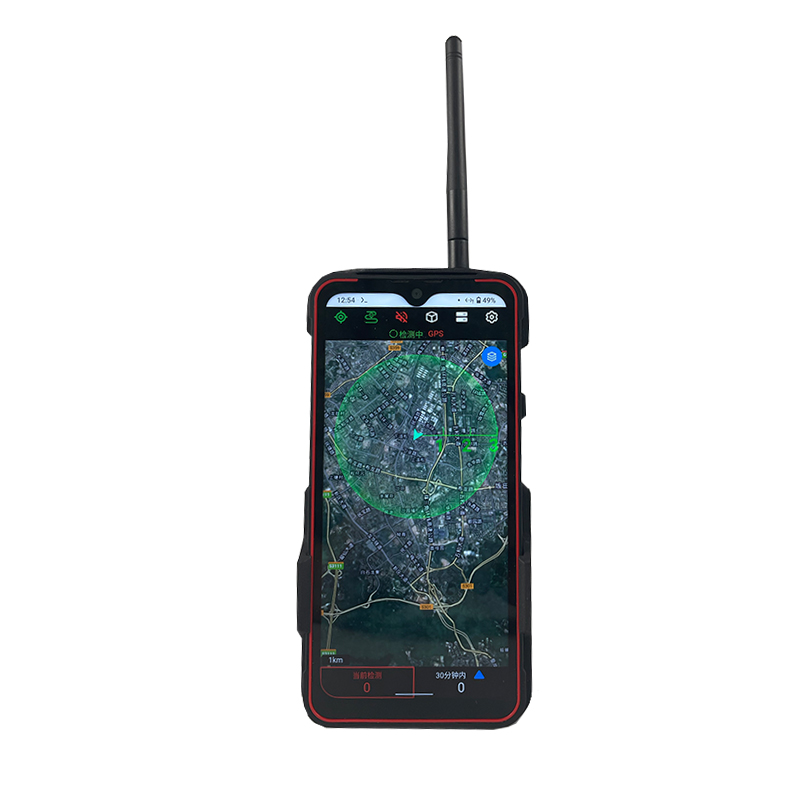
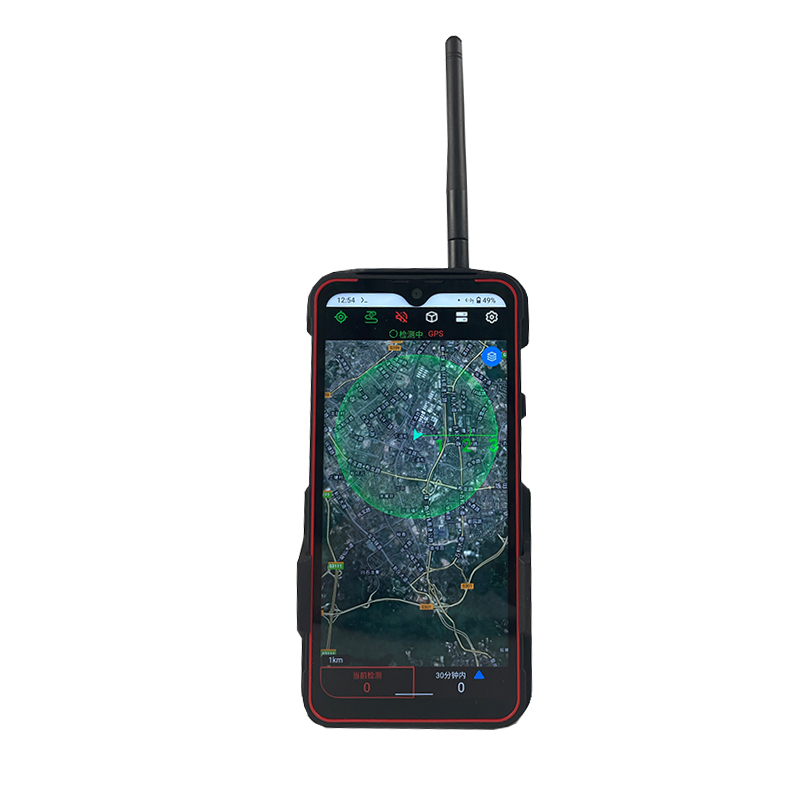
Airspace Security Alert! Is Your Territory Still Safe?
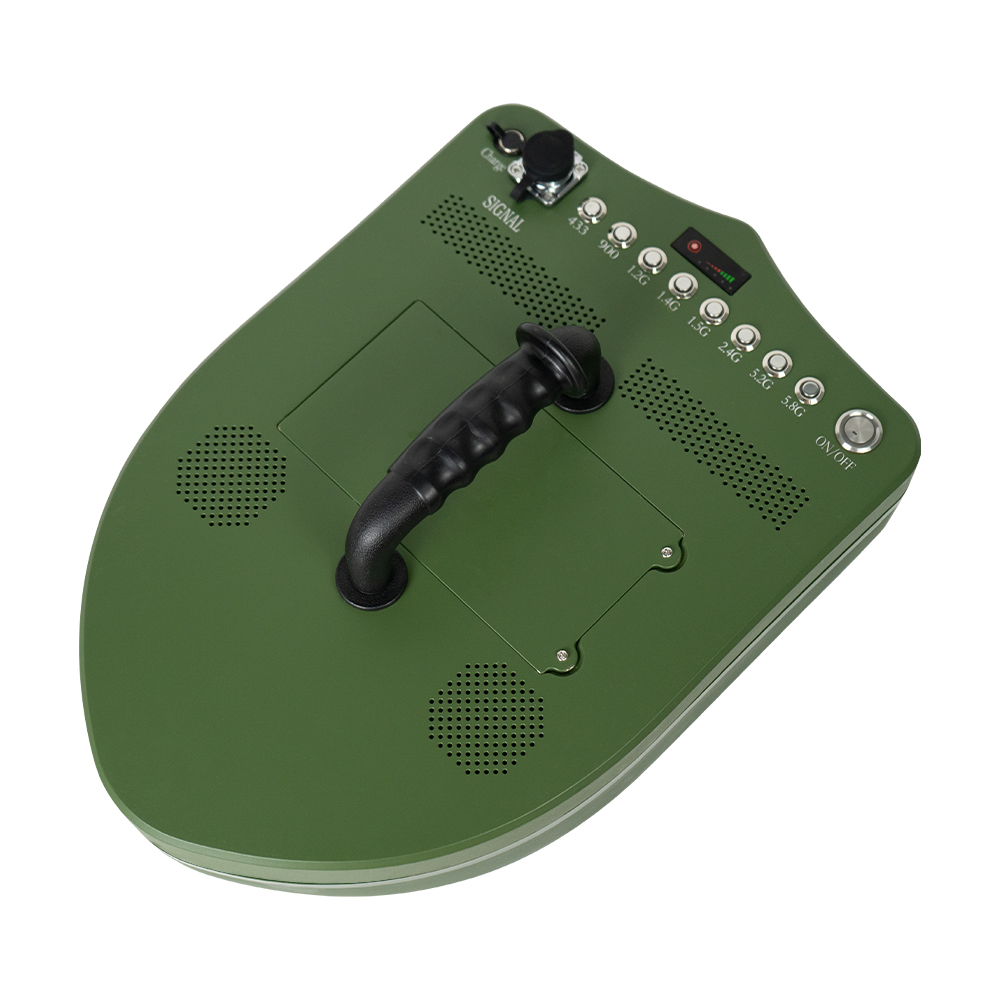
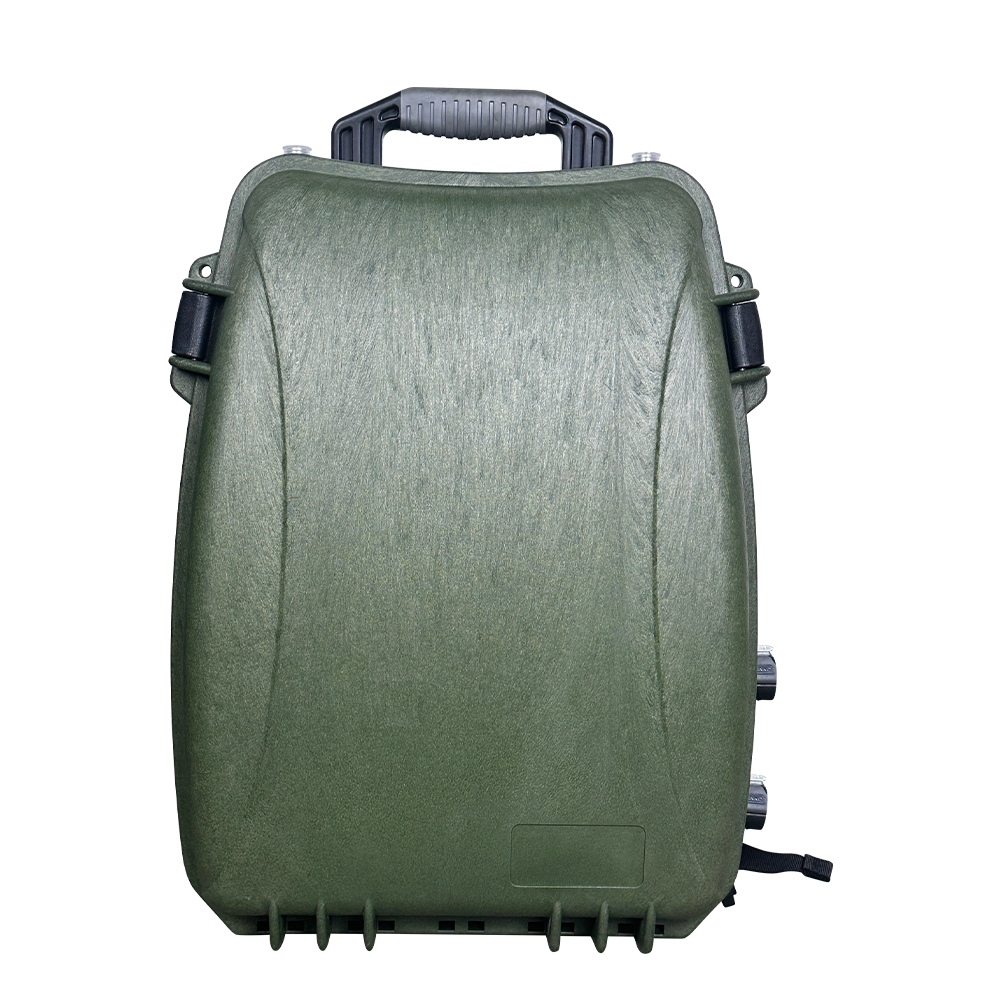
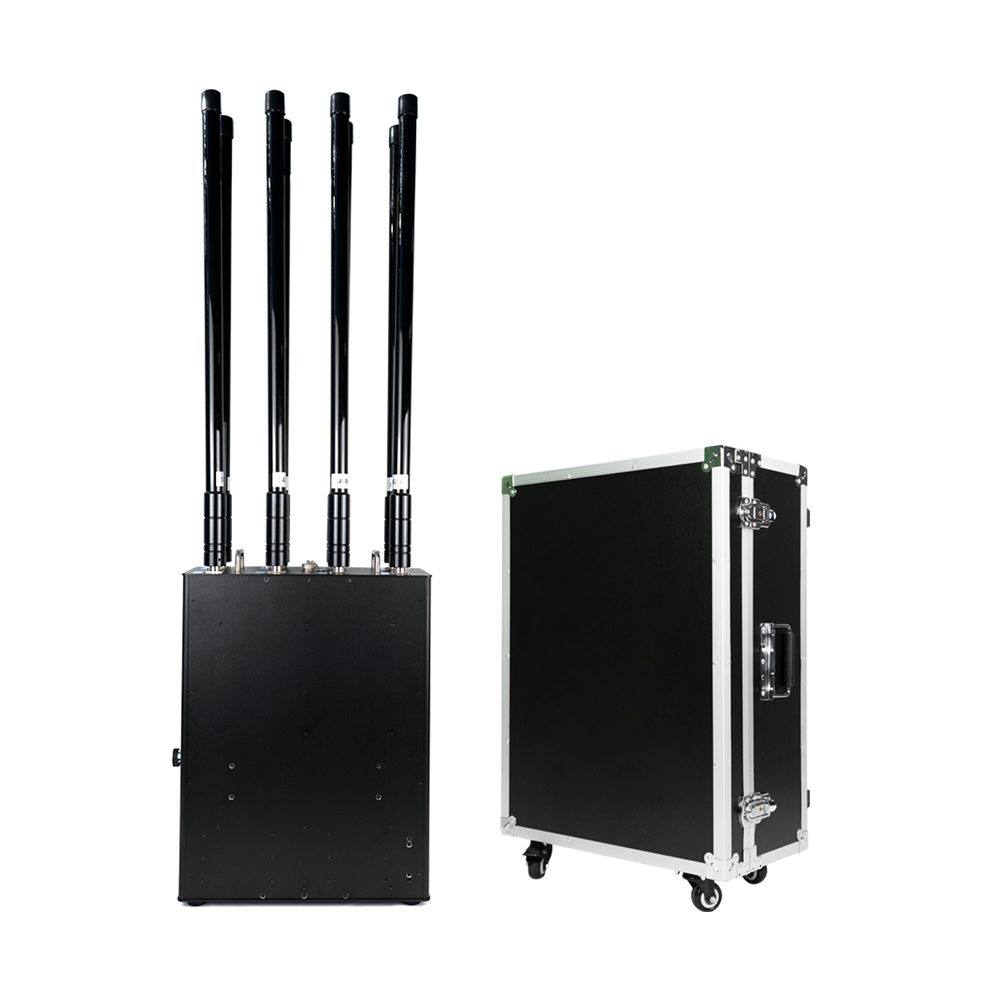
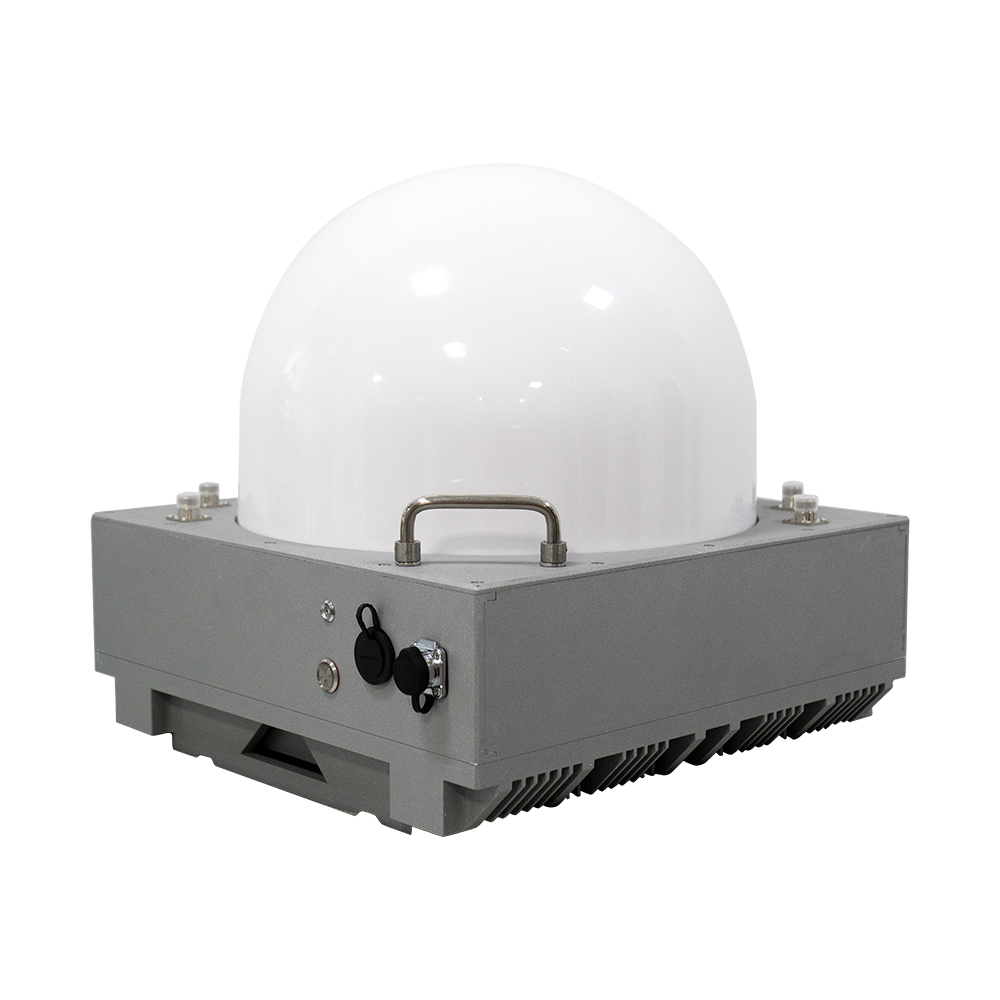
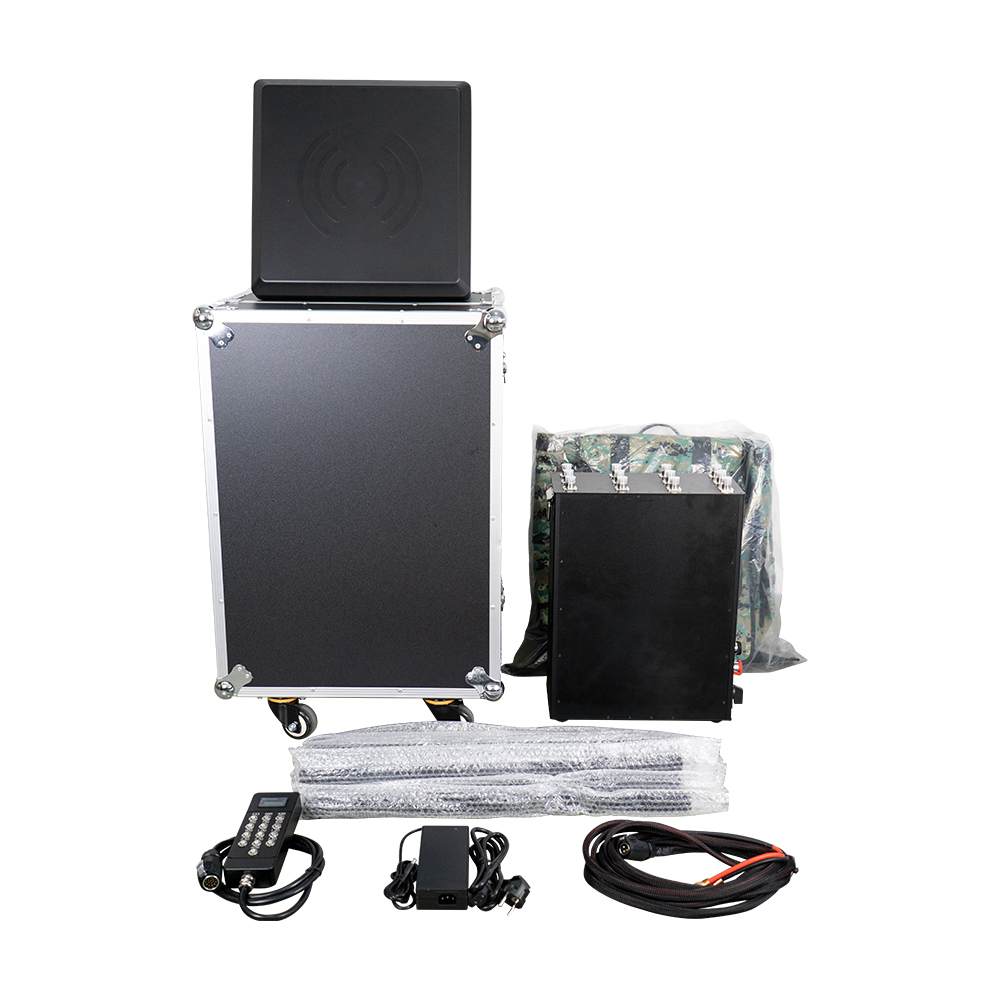
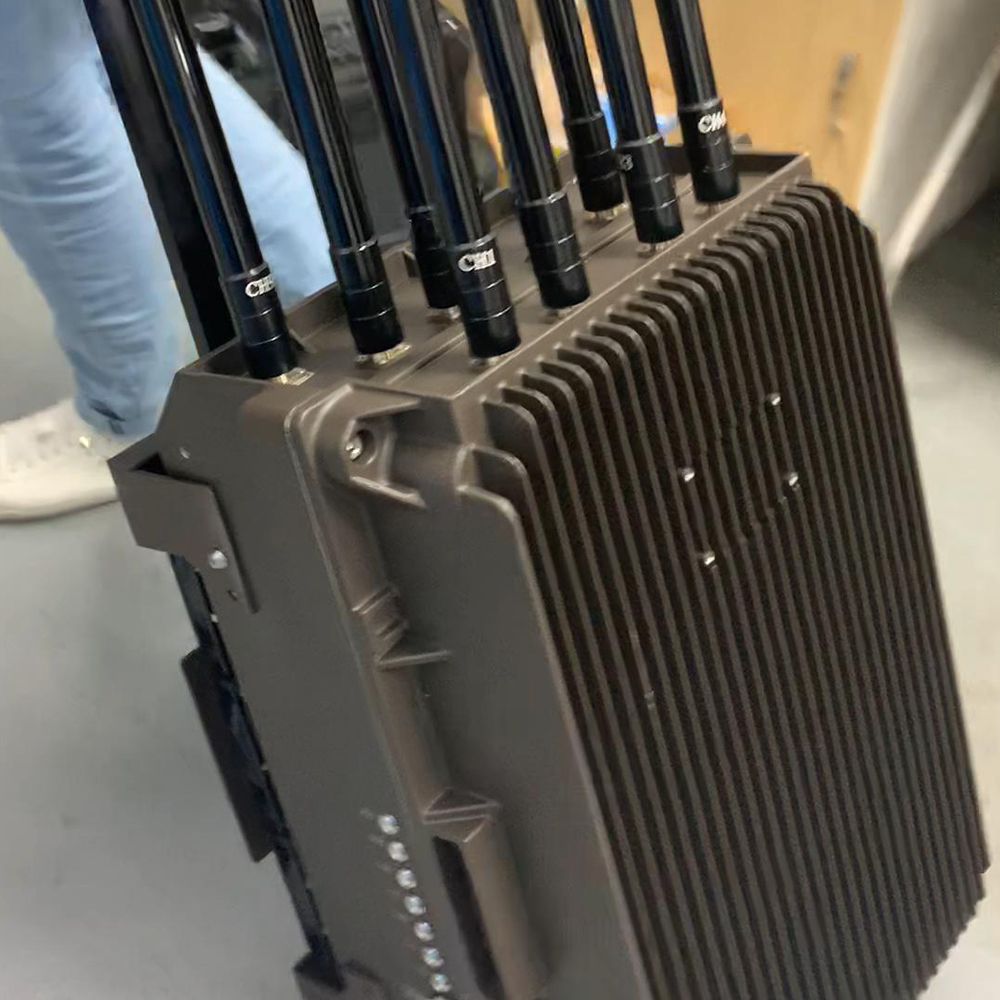
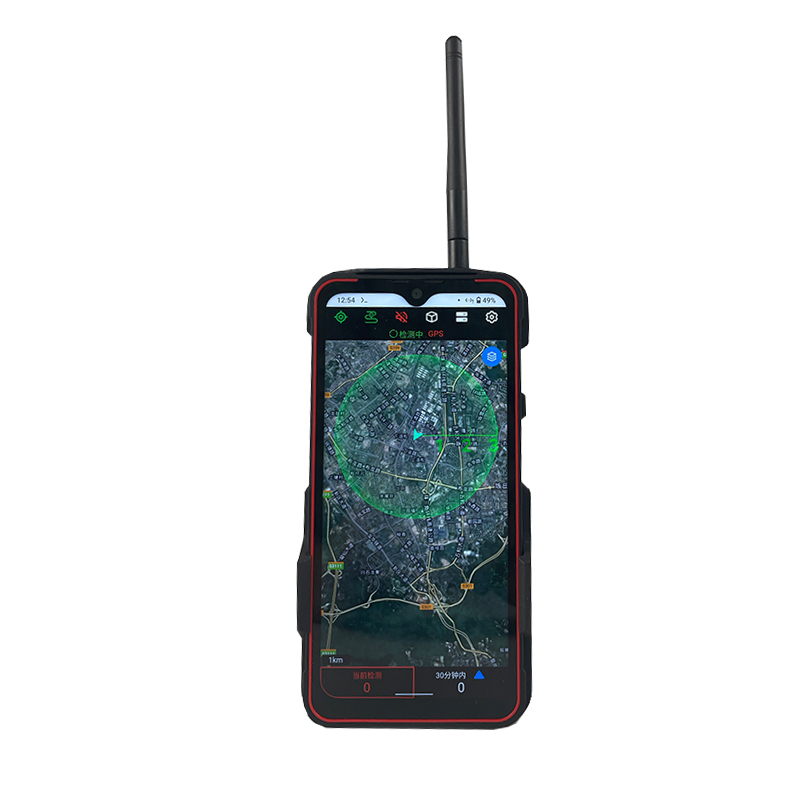
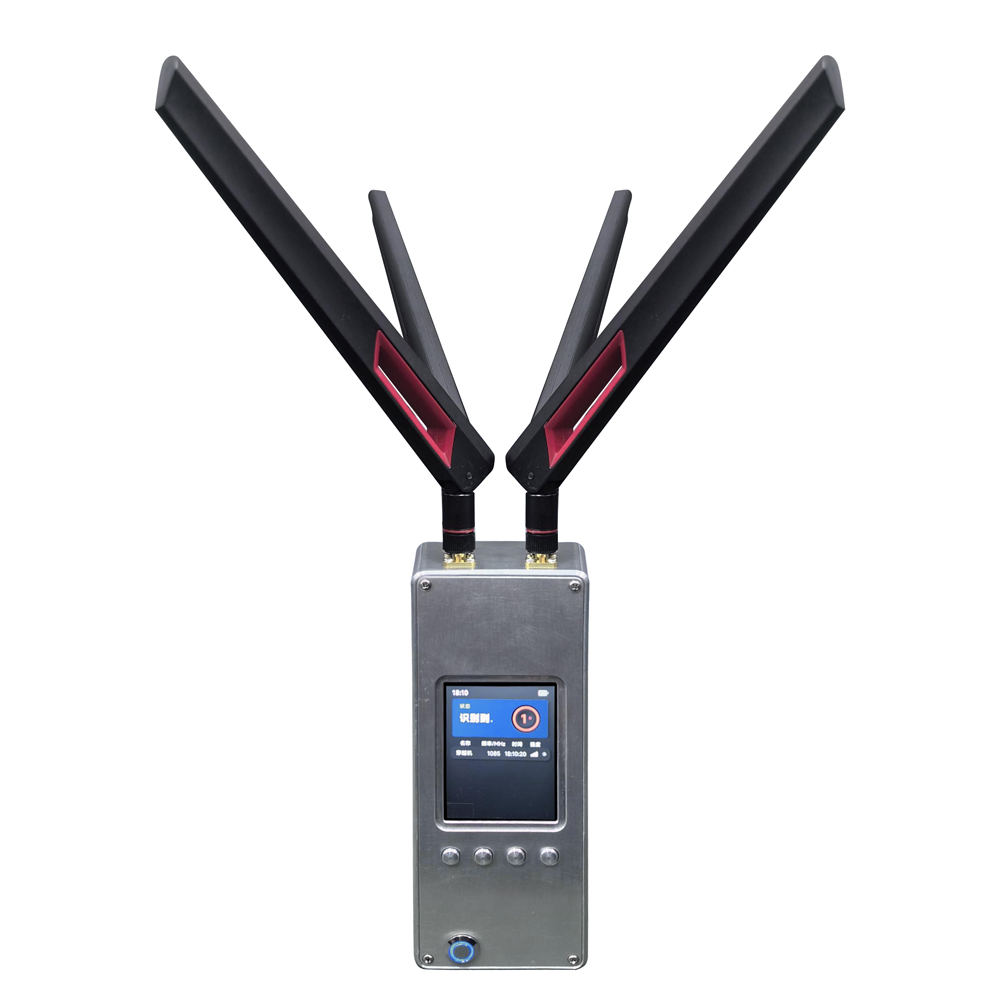
The Omni-Smart Counter-Drone System: Your Invisible Shield! When drones infiltrate silently, the threat looms overhead! Imagine this: At a high-profile international event, an unidentified drone suddenly breaches the core zone, disrupting live broadcasts and throwing the venue into chaos. In a heavily fortified prison, drones deliver contraband under cover of darkness, challenging security limits. At a bustling airport, rogue drones cause massive flight delays, costing millions per second. Even your private estate or corporate campus could become a target for surveillance or malicious disruption… Drone threats are no longer sci-fi—they’re here! Small, fast, and agile, they evade traditional security measures. Every “black flight” risks escalating into a security disaster, catastrophic loss, or a crisis of trust. Are you prepared? The Omni-Smart Counter-Drone System: Your “Aerial Guardian” Is On Standby! We understand your uncompromising demand for safety. Introducing the next-generation Omni-Smart Counter-Drone System—not just a jammer, but a comprehensive, intelligent airspace security solution integrating precision detection, AI-driven identification, multi-layered countermeasures, and end-to-end tracking. We build a closed-loop defense shield from “detection” to “neutralization.” Core Strengths: Forging an Ironclad Defense “Eagle-Eye” Detection: Zero Blind SpotsMulti-Sensor Fusion: Seamlessly integrates advanced radar, radio frequency monitoring, HD electro-optical tracking, and AI vision recognition to detect drones across all terrains—day or night, rain or shine. Early warnings enable proactive responses. AI-Powered Identification: Pinpoint AccuracySmart Target Discrimination: Machine learning algorithms instantly distinguish between friendly drones (e.g., delivery UAVs) and hostile threats. Eliminate false alarms with >99% precision. Focus resources where they matter most. Multi-Tiered Countermeasures: Adaptive NeutralizationFlexible Response Toolkit: Deploy targeted radio frequency jamming, GPS spoofing, or safe drone capture based on threat levels. Force unauthorized drones to land, return to origin, or be immobilized—without collateral damage. Centralized Command & Control: Total Situational AwarenessIntuitive Command Center: Real-time 3D visualization displays drone trajectories, threat levels, and response status. One-click coordination with law enforcement or security teams ensures seamless, decisive action. Who Needs This? Securing Critical Frontlines Government & Military:Government complexes, military bases, borders, prisons—defend national security against espionage and sabotage. Industrial & Commercial Facilities:Petrochemical plants, manufacturing hubs, R&D centers, luxury communities—safeguard operations, trade secrets, and privacy. Public Safety:Counter-terrorism, crowd control at events, disaster management—enhance emergency response and protect civilians. Choose Us: Choose Confidence & Expertise Cutting-Edge Technology:Continuous R&D partnerships with leading institutions keep us at the industry forefront. Battle-Proven Reliability:Deployed in high-stakes security projects worldwide—trusted where failure is not an option. Tailored Solutions:We analyze your unique risks, delivering end-to-end services from risk assessment to deployment and training. Unwavering Support:24/7 technical assistance and maintenance ensure your system operates flawlessly, always on guard. Airspace security can’t wait! Every moment of vulnerability invites risk. Act now—fortify your skies with an impenetrable defense!

Core Accessory Matrix: Military DNA + Million-Unit Validation, Performance Revolutionized
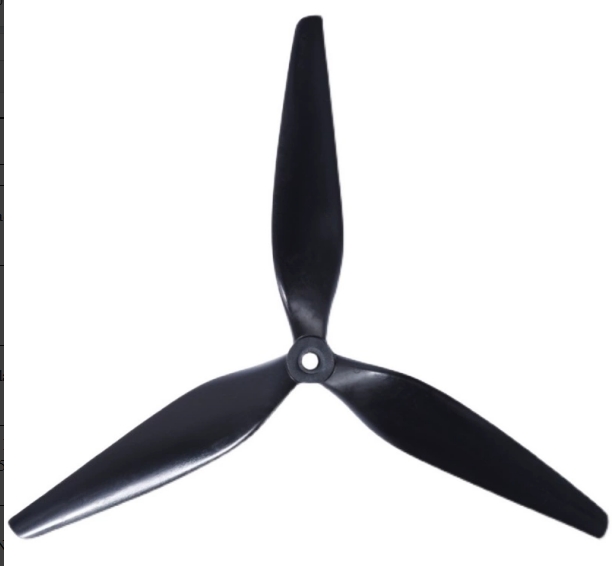
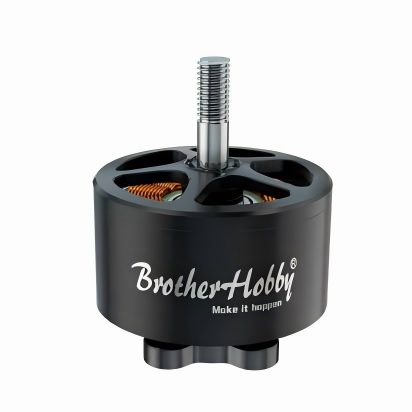
Core Accessory Matrix: Military DNA + Million-Unit Validation, Performance Revolutionized 1. Carbon Fiber Frame: Direct from Shenzhen Military-Grade Factory, Ultimate Balance of Lightweight & RigidityModel: 10 inch MARK4 V2Hardcore Capabilities:✅ Military-Grade Carbon Fiber Craftsmanship: Produced by Shenzhen-designated carbon fiber processing facility with annual capacity exceeding 1 million units. Material strength meets aerospace standards.✅ Structurally Optimized Design: 30% weight reduction while impact resistance increased by 50%. Delivers rock-solid stability during extreme flight maneuvers. 2. Flight Tower System: ST MCU + High-Spec MOSFETs, Million-Unit Fault-Free Operation VerifiedConfiguration: F405 V3 Flight Controller + ESC-70A ESCTechnical Barriers:⚡️ Anti-Interference Flight Controller: ST industrial-grade MCU ensures zero signal loss in complex electromagnetic environments.⚡️ High-Efficiency ESC: High-voltage MOSFETs deliver stable, reliable current output – supporting aggressive endurance and instantaneous burst power. 3. Power Core: Tech-Sharp 3115 Motors, Global 10-Million-Unit Sales CertifiedModel: 3115 900KV Brushless Motor (4PCS/Set)Performance Breakthroughs:🚀 One-Piece Molding Process: Calibrated with Tech-Sharp DC motor technology – response time as fast as 0.01 seconds.🚀 10 Million Units Annual Production/Sales: Proven reliability in global markets – consistent power output over extended use. 4. Video Transmission System: Tuned by ZTE Team, Dominant Model in Russian MarketModel: RUSH 5.8G-2.5WTransmission Revolution:📡 Military RF Solution: High-performance chips + ZTE team’s deep optimization – 300% improvement in anti-interference capability.📡 Ultra-Long-Range Stable Transmission: 2.5W high power – industry-leading signal penetration in complex terrains. 5. Propellers: Beihang Aerodynamic Design, Dual Breakthrough in Lift & EfficiencySpec: 10x50x3 Black Engineering Nylon Propellers (4PCS/Set)Black-Tech Empowerment:✈️ Beihang Expert-Led Aerodynamic Design: 40% increase in lift factor – simultaneous optimization of payload capacity and speed.✈️ Military-Grade Materials: Special nylon compound – tear resistance 5x stronger than standard propellers. Industry-Grade Expansion Solutions: Fiber Optic Transmission + Smart Terminals, Breaking Distance & Environmental Barriers 6. 10KM Fiber Optic Transmission System: Developed by Military Institute Team, Beyond-Visual-Range Operations ToolConfiguration: Airborne Module + Ground Terminal Module (GBD)Disruptive Advantages:🔹 10km Lossless Transmission: 1310nm-1550nm fiber band – zero electromagnetic interference, zero signal latency.🔹 Military-Grade Reliability: Nearly 100,000 units deployed in field operations – battle-tested in forest inspections and border security. 7. Smart Ecosystem Accessories: End-to-End Professional Support from Battery to Control 9000mAh 100C Battery: High-cobalt formula – stable discharge from -20°C to 60°C. Annual sales exceed 1 million units. 150W Smart Fast Charger: Dynamic battery diagnostics – 60% faster charging, 30% extended lifespan. TX12 ELRS Transmitter: 915MHz protocol, 500mw ultra-low latency – frontline operational-grade control experience. VR Goggles: 800-line HD display + 5.8G high-gain antenna – immersive, zero-lag flight visuals. Upgrade Your FPV Ecosystem Now!Whether for extreme racing, industrial inspection, or security reconnaissance – the FPV-10” full accessory series safeguards your professional flights with military-grade quality, mass-production scalability, and cutting-edge performance!

Professional FPV Flight Experience: Choose the Right Equipment
In today's drone flying community, the First-Person View (FPV) experience is becoming increasingly popular. Whether you're a professional racing pilot or a hobbyist who loves aerial photography, everyone wants to achieve clear and stable real-time video transmission through high-quality FPV equipment. This allows for better drone control and the ability to capture amazing moments. Today, let's take a closer look at three exceptional FPV devices: the RFVTX-T67 (6–7GHz Transmitter), the RFVRX-R67 (6–7GHz Receiver), and the 4.9/5.8GHz 2.5W VTX (Dual-Band Transmitter). Discover how they can enhance your flying journey. RFVTX-T67: The Powerful 6–7GHz Transmitter The RFVTX-T67 is a 6–7GHz transmitter designed specifically for FPV enthusiasts who demand top performance. With 64 selectable channels, it can easily handle complex and varied flying environments, effectively avoiding signal interference and ensuring stable and smooth video transmission no matter where you fly. Its power is adjustable between 25–3000mW, catering to both close-range precision control and long-range exploration. Moreover, this transmitter is equipped with an efficient cooling fan and an SMA connector, along with an intuitive on-screen menu that makes setup a breeze, eliminating any worries about complicated procedures. Imagine yourself in an intense FPV racing competition, maneuvering your drone through narrow tracks where every turn and obstacle requires precise judgment and quick reactions. At such moments, the RFVTX-T67, with its robust signal transmission capabilities and stable performance, delivers high-definition footage in real-time to your display. It makes you feel as if you're inside the drone, experiencing the perfect blend of speed and excitement. Whether it's the slightest vibrations during high-speed flight or the breathtaking panoramic views from a distance, everything is clearly presented before your eyes, giving you an edge in the race and helping you easily overtake your opponents. RFVRX-R67: The High-Sensitivity 6–7GHz Receiver The perfect match for the RFVTX-T67 is the RFVRX-R67, a 6–7GHz video receiver. It has 40 channels that can accurately receive signals from the transmitter, ensuring stable and smooth video transmission. With a sensitivity of -96dBm, it can capture even the weakest signals, providing you with clear images. Moreover, this receiver boasts a frequency stability of ±100kHz and a wide input voltage range of +7–28V, allowing it to maintain excellent performance during long-range transmission and providing reliable support for your FPV flights. When you're flying outdoors, you may encounter various complex terrains and environmental factors, such as mountains and building obstructions, which can interfere with signal transmission. However, the RFVRX-R67, with its outstanding performance, can easily tackle these challenges. It can stably receive signals from the transmitter in various complex environments, eliminating concerns about signal loss or video lag during flight. Whether you're flying between urban skyscrapers or exploring vast fields and forests, the RFVRX-R67 delivers clear and stable images, allowing you to fully enjoy the pleasure of flying. 4.9/5.8GHz 2.5W VTX: The Versatile Dual-Band Transmitter In addition to the 6–7GHz devices, the 4.9/5.8GHz 2.5W VTX dual-band transmitter offers even more options for your FPV flights. This transmitter supports both the 4.9GHz and 5.8GHz bands, with 8+48 channels available, meeting the diverse needs of different users in various scenarios. Its maximum power output of 2.5W provides longer transmission distances and stronger signal penetration, enabling you to freely explore broader areas during your flights. The 4.9/5.8GHz 2.5W VTX employs the advanced IRC Tramp protocol to ensure efficient and stable signal transmission. It also features an SMA connector and an aluminum casing, along with an efficient cooling fan. These components not only ensure stable operation over extended periods but also enhance the device's durability and longevity. Whether you need to fly at low altitudes in urban areas or explore high-altitude regions in the mountains, the 4.9/5.8GHz 2.5W VTX will provide reliable signal transmission support, making your flights more effortless and enjoyable. Combining These Devices for the Ultimate FPV Experience These three devices not only have outstanding individual performance but also create a powerful synergy when used together. You can pair the RFVTX-T67 with the RFVRX-R67 to form a complete 6–7GHz FPV transmission system, enjoying stable and high-definition video transmission. When you need broader frequency coverage, the 4.9/5.8GHz 2.5W VTX offers more options, allowing you to switch frequencies flexibly according to different flight scenarios to achieve the best possible signal transmission. Whether you're participating in professional FPV racing competitions or exploring with aerial photography in your spare time, these three devices can meet your needs. Their high performance and stability will bring you an unparalleled flying experience, allowing you to soar freely in the sky and capture every amazing moment. Choose these devices to embark on your professional FPV flight journey and make every flight an unforgettable memory.

Siemens Chips: The “Core” Power of Intelligent Technology
In today’s digital age, where the wave of digitalization is sweeping across the globe, chips, as the core components of modern technology, are playing an unprecedentedly crucial role. Siemens, a global technology giant with profound experience in industrial automation, intelligent manufacturing, and digitalization, has introduced Siemens chips, which are undoubtedly the shining stars in this field and are injecting powerful “core” power into the intelligent transformation of various industries. Exceptional Performance Empowers Intelligent Manufacturing Adopting advanced manufacturing processes, Siemens chips boast exceptional computing power and low power consumption. In the field of industrial automation, these chips can quickly handle complex data tasks, support high-precision sensor data acquisition, and real-time control, thereby realizing the efficient automation and intelligentization of production processes. Whether it is precision mechanical manufacturing or complex chemical production processes, Siemens chips can ensure the stable operation and precise control of equipment, significantly improving production efficiency and product quality. High Integration Facilitates the Development of the Internet of Things With the rapid development of the Internet of Things (IoT), the interconnectivity of devices has become a key demand. The highly integrated design of Siemens chips enables them to easily integrate multiple functional modules, such as communication modules, sensor interfaces, and data processing units. This not only reduces the size and cost of devices but also enhances the reliability and flexibility of the system. Through these chips, various smart devices can seamlessly connect to IoT platforms, enabling real-time data transmission and sharing. This provides solid technical support for applications in smart homes, smart cities, and industrial IoT. Safety and Reliability Guard Data Security In the digital era, data security is of vital importance. Siemens chips are equipped with advanced security mechanisms that can effectively prevent data leakage and malicious attacks. Their encryption technology ensures the security of data during transmission and storage, while hardware-level security authentication provides reliable protection for device identity verification. Whether it is sensitive data in industrial control systems or user privacy in IoT devices, Siemens chips can offer comprehensive security protection, allowing users to use them with confidence. Wide Applications Drive Industry Innovation The application scope of Siemens chips is extremely broad, covering multiple fields such as industrial automation, intelligent manufacturing, the Internet of Things, and automotive electronics. In the automotive electronics field, Siemens chips provide powerful computing support for autonomous driving and intelligent driving assistance systems, helping the automotive industry transform towards intelligence and electrification. In the medical equipment field, these chips can support high-precision medical imaging processing and remote medical monitoring, providing strong support for the digital upgrade of the medical industry. Choose Siemens Chips to Embrace a Smart Future Choosing Siemens chips means partnering with a global leading technology company to jointly embrace a smart future. Siemens not only offers high-performance chip products but also provides comprehensive technical support and customized solutions. Whether you are a large manufacturing enterprise or an innovative technology company, Siemens can provide the most suitable chip products and solutions according to your needs, helping to drive your business development and technological innovation. Siemens chips, with their exceptional performance, high integration, and reliable security, are providing powerful momentum for the digital transformation of various industries. Let’s join hands with Siemens to step into a future that is smarter, more efficient, and safer.
Innovation-Driven, Superior Performance: Exploring Domestic Alternatives to Linear Technology Chips
In the rapidly evolving field of electronics, the chip serves as the heart of electronic products, and its performance and reliability are crucial. We understand that many businesses and developers are looking for chip solutions that offer excellent performance and cost-effectiveness. Today, we are proud to introduce our domestic alternatives to Linear Technology chips, which not only meet your needs but also provide additional performance advantages and technical support. Why Choose Our Alternative Chips? Performance Matching and Surpassing: Our alternative chips match the performance indicators of Linear Technology chips in many aspects, and even surpass them in key parameters such as efficiency and junction temperature. This means you can expect the same stable performance as the original chips while enjoying higher efficiency and reliability. Technological Innovation: Our chips not only achieve drop-in replacement but also innovatively integrate four Schottky diodes and a temperature sensor. This technological innovation allows our chips to improve while providing a quick replacement, truly becoming the pride of domestic chips. Autonomy and Control: In today's increasingly complex global supply chain, choosing domestic chips means you can reduce dependence on external supply chains and increase the autonomy and security of your products. Cost Advantage: Domestic production not only reduces manufacturing costs but also allows military equipment to obtain products of the same quality at more affordable prices. This helps save military project funds and improve economic benefits. Environmental Protection: While pursuing technological innovation, we also do not forget our environmental responsibilities. Our chips use environmentally friendly materials and energy-saving technologies, reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions, allowing you to contribute to protecting the Earth's environment while enjoying the benefits of technology. Wide Application Field: Whether it's commercial aerospace power modules, in-vehicle electronic rearview mirrors, radar signal processing, or flight control systems, our alternative chips can provide strong support. Conclusion: By choosing our Linear Technology chip alternatives, you will gain a solution that offers superior performance, cost-effectiveness, and environmental protection. Contact us today to learn more about our alternative chips, and let us work together to promote technological innovation and create a better future.

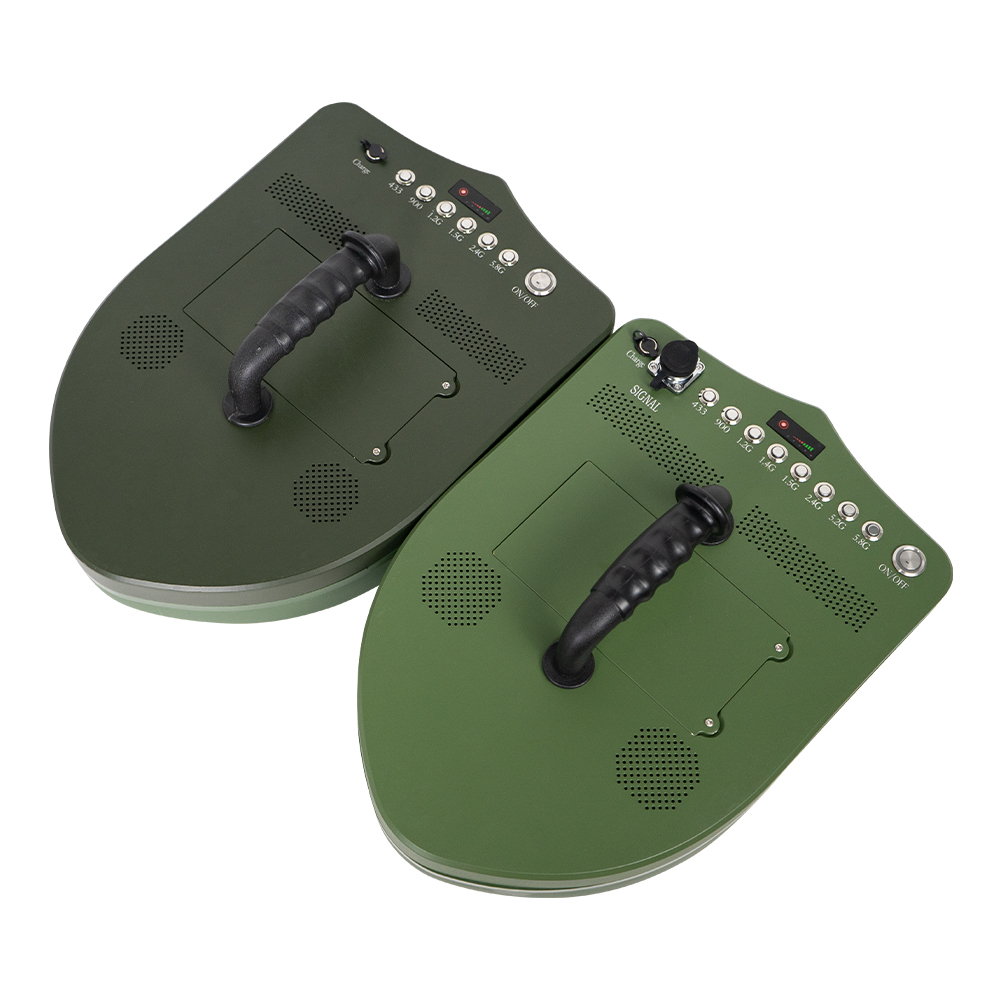
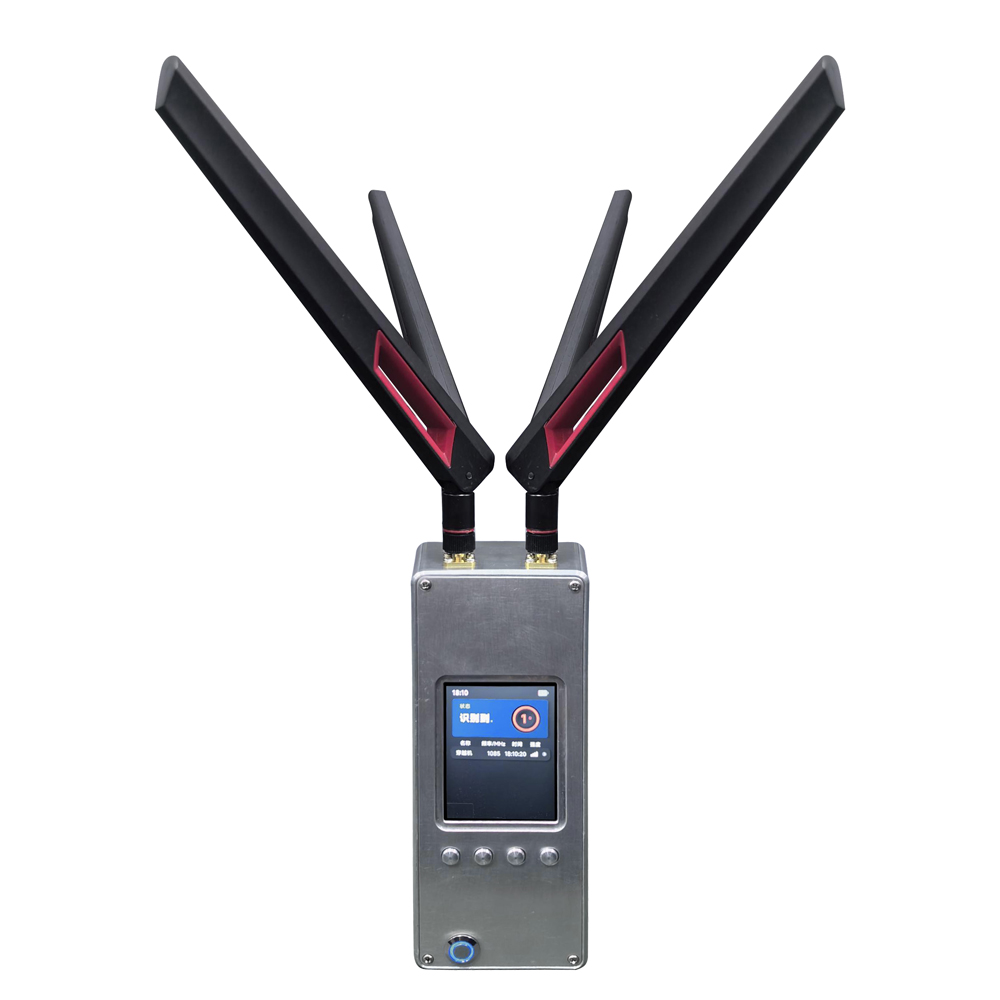
Advanced Anti-Drone Devices – The Future of Airspace Security
Advanced Anti-Drone Devices – The Future of Airspace Security In recent years, drones have become widely used for photography, logistics, agriculture, and entertainment. However, unauthorized drones also pose serious risks to airports, borders, government facilities, events, and private properties. This has created a strong demand for anti-drone devices that can detect, track, and neutralize UAV threats effectively. What is an Anti-Drone Device? An anti-drone device, also known as a counter-UAV system or drone jammer, is designed to detect and disrupt drones in restricted areas. These devices use radio frequency (RF) jamming, GPS signal blocking, or radar detection to prevent drones from flying near sensitive locations. How Anti-Drone Devices Work 1.Drone Detection – Using radar, RF sensors, or cameras, the system identifies unauthorized drones. 2.Signal Jamming – The device blocks communication between the drone and its controller by disrupting RF or GPS signals. 3.Neutralization – The drone either lands safely or returns to its take-off point. Key Features of Our Anti-Drone Solutions ✅ Real-time UAV detection & tracking ✅ RF & GPS signal jamming for long distances ✅ Portable or fixed installation options ✅ Military-grade technology for security and defense Applications of Anti-Drone Devices 🔹 Airports & Aviation Security – Prevent drones from interfering with flights. 🔹 Military & Border Protection – Secure sensitive areas from drone spying. 🔹 Government & VIP Events – Block drones from unauthorized filming or attacks. 🔹 Critical Infrastructure – Protect power plants, oil refineries, and data centers. 🔹 Prisons & Private Properties – Stop drones from smuggling or surveillance. Why Choose Our Anti-Drone Technology? Our anti-drone devices combine advanced radar detection with high-performance jamming technology, offering reliable protection against unauthorized UAVs. With portable and stationary models, they are suitable for both military and commercial applications. If you are looking for a powerful counter-drone solution, contact us today for customized anti-drone systems to secure your airspace.
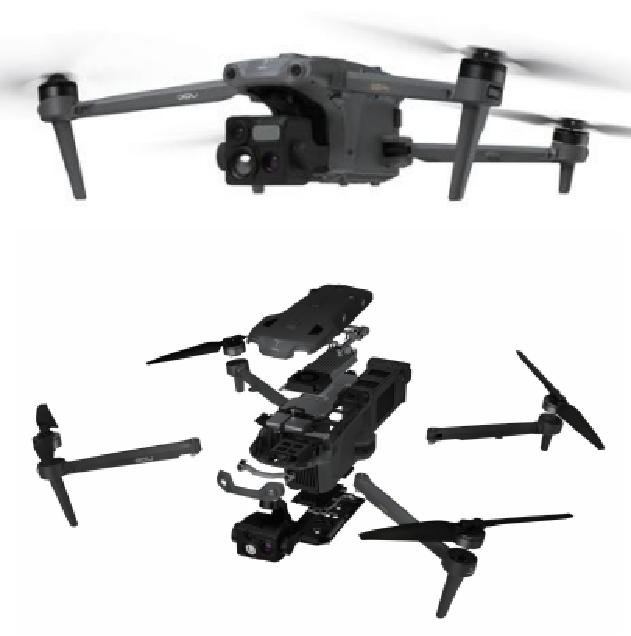
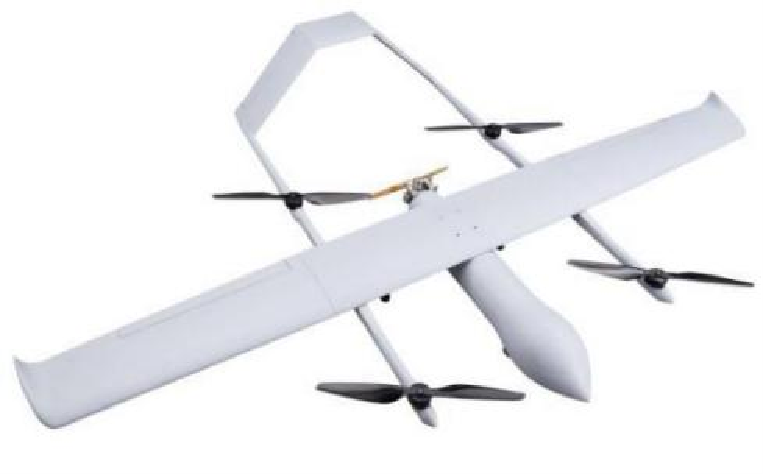


































 IGBT/module
IGBT/module