Airspace Security Alert! Is Your Territory Still Safe?
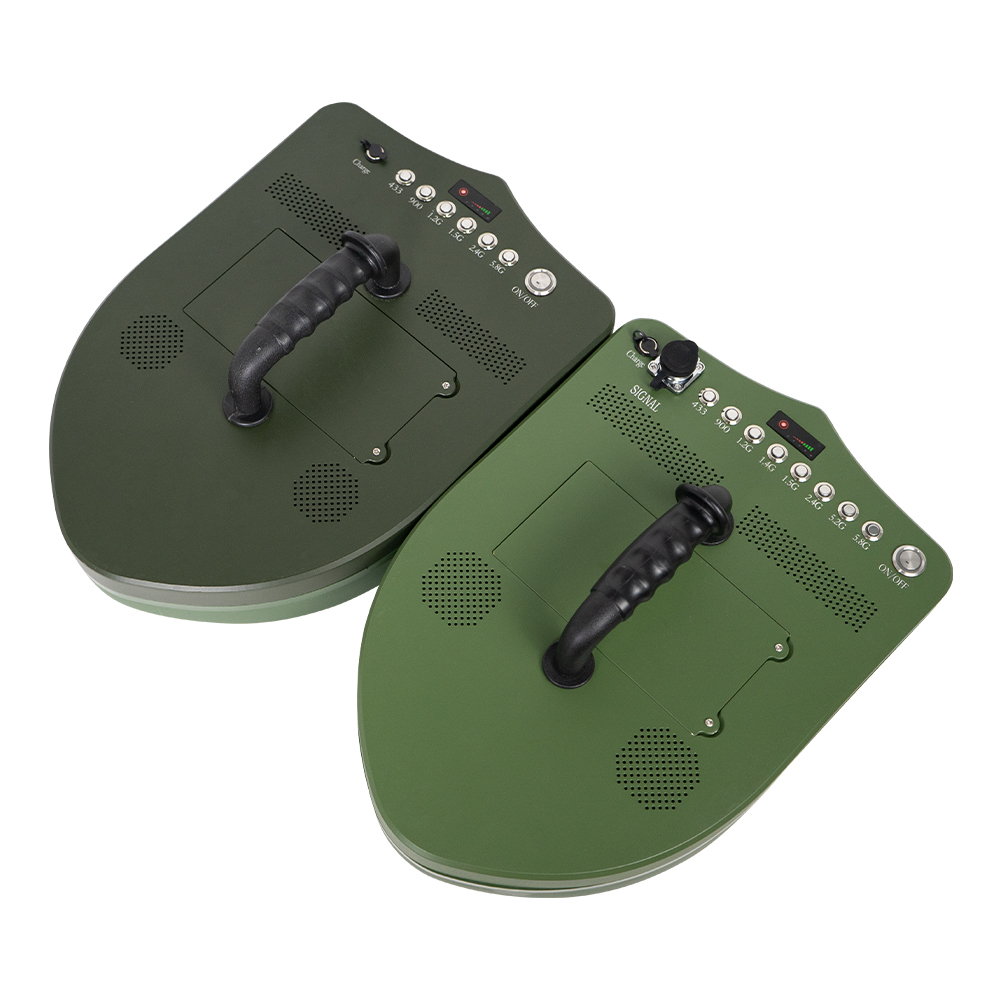
The Omni-Smart Counter-Drone System: Your Invisible Shield! When drones infiltrate silently, the threat looms overhead! Imagine this: At a high-profile international event, an unidentified drone suddenly breaches the core zone, disrupting live broadcasts and throwing the venue into chaos. In a heavily fortified prison, drones deliver contraband under cover of darkness, challenging security limits. At a bustling airport, rogue drones cause massive flight delays, costing millions per second. Even your private estate or corporate campus could become a target for surveillance or malicious disruption… Drone threats are no longer sci-fi—they’re here! Small, fast, and agile, they evade traditional security measures. Every “black flight” risks escalating into a security disaster, catastrophic loss, or a crisis of trust. Are you prepared? The Omni-Smart Counter-Drone System: Your “Aerial Guardian” Is On Standby! We understand your uncompromising demand for safety. Introducing the next-generation Omni-Smart Counter-Drone System—not just a jammer, but a comprehensive, intelligent airspace security solution integrating precision detection, AI-driven identification, multi-layered countermeasures, and end-to-end tracking. We build a closed-loop defense shield from “detection” to “neutralization.” Core Strengths: Forging an Ironclad Defense “Eagle-Eye” Detection: Zero Blind SpotsMulti-Sensor Fusion: Seamlessly integrates advanced radar, radio frequency monitoring, HD electro-optical tracking, and AI vision recognition to detect drones across all terrains—day or night, rain or shine. Early warnings enable proactive responses. AI-Powered Identification: Pinpoint AccuracySmart Target Discrimination: Machine learning algorithms instantly distinguish between friendly drones (e.g., delivery UAVs) and hostile threats. Eliminate false alarms with >99% precision. Focus resources where they matter most. Multi-Tiered Countermeasures: Adaptive NeutralizationFlexible Response Toolkit: Deploy targeted radio frequency jamming, GPS spoofing, or safe drone capture based on threat levels. Force unauthorized drones to land, return to origin, or be immobilized—without collateral damage. Centralized Command & Control: Total Situational AwarenessIntuitive Command Center: Real-time 3D visualization displays drone trajectories, threat levels, and response status. One-click coordination with law enforcement or security teams ensures seamless, decisive action. Who Needs This? Securing Critical Frontlines Government & Military:Government complexes, military bases, borders, prisons—defend national security against espionage and sabotage. Industrial & Commercial Facilities:Petrochemical plants, manufacturing hubs, R&D centers, luxury communities—safeguard operations, trade secrets, and privacy. Public Safety:Counter-terrorism, crowd control at events, disaster management—enhance emergency response and protect civilians. Choose Us: Choose Confidence & Expertise Cutting-Edge Technology:Continuous R&D partnerships with leading institutions keep us at the industry forefront. Battle-Proven Reliability:Deployed in high-stakes security projects worldwide—trusted where failure is not an option. Tailored Solutions:We analyze your unique risks, delivering end-to-end services from risk assessment to deployment and training. Unwavering Support:24/7 technical assistance and maintenance ensure your system operates flawlessly, always on guard. Airspace security can’t wait! Every moment of vulnerability invites risk. Act now—fortify your skies with an impenetrable defense!
2025-08-14 10:40:27